GC
GC Solare Universal Bond
GC Solare Universal Bond
Couldn't load pickup availability
GC Solare Bond Universal
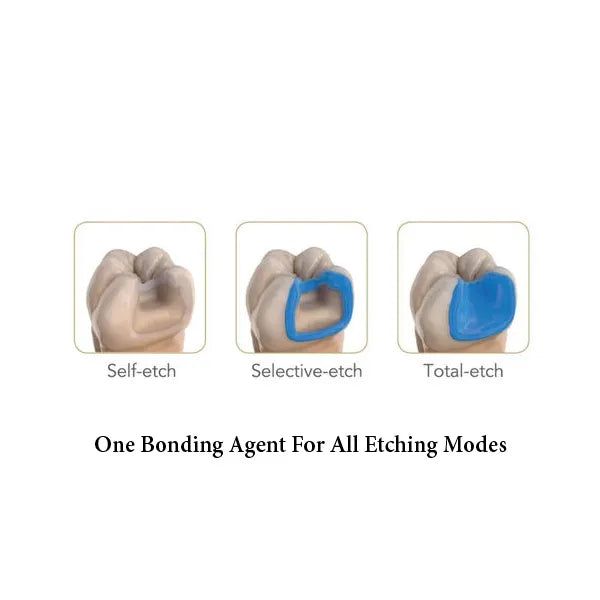
Superior bond strength of Solare Universal Bond to enamel and dentine is attributable to its unique formulation. The Di methacrylate monomer in Solare Universal bond increases its permeability into enamel and dentine covered to another adhesives, while the increased level of phosphate ester monomer optimises etching.
INDICATIONS
- Bonding of light cured composites and acid modified composites (compomers) to tooth structure.
- Bonding of dual cured luting and core build up composites to tooth structure as long as these materials are light cured.
Features
Features
- High radio-opacity even at low thickness
- Excellent handling properties
- Optimal durability
Description
Description
Specification
Specification
- Store at room temperature (1-28°C) (33.8-82.4°F)
Packaging
Packaging
GC Solare Universal Bond
- 1 x 2.5ml Bottle
- 1 x 5ml Bottle
Direction to use
Direction to use
- Step 1: Apply SOLARE UNIVERSAL BOND to the tooth surface.
- Step 2: Leave undisturbed for 10s
- Step 3: Dry thoroughly for 5s under maximum air pressure
- Step 4: Light Cure for 10s
Additional info
Additional info
Warranty
Warranty
Product Related Questions
Product Related Questions
Question: Does GC Solare Universal Bond contain 10-methacryloyloxydecyl dihydrogen phosphate (10-MDP)?
Answer: Yes, GC Solare Universal Bond contains 10-methacryloyloxydecyl dihydrogen phosphate (10-MDP). This component enhances the bond strength and provides excellent durability, making it suitable for a wide range of dental restorative applications.
Question: What are the key features of GC Solare Universal Bond?
Answer: GC Solare Universal Bond offers several key features that make it a valuable addition to dental practices. It provides high bond strength, ensuring the stability of restorations. This bonding agent also exhibits excellent handling properties, allowing for precise placement and adaptation. Its compatibility with a wide range of restorative materials makes it a versatile and reliable choice for various dental applications.
Question: How is GC Solare Universal Bond applied in dental procedures?
Answer: GC Solare Universal Bond is applied to the prepared tooth surface before the placement of restorative materials. It creates a strong and durable bond, ensuring the stability of the restoration. This bonding agent is specially formulated to work with various restorative materials, providing optimal results.
Question: What is GC Solare Universal Bond?Answer: GC Solare Universal Bond is a versatile dental bonding agent . It is designed for use with a wide range of restorative materials, providing reliable adhesion. This product is known for its ease of use and effectiveness in achieving durable dental restorations.
Question: How should I store GC Solare Universal Bond?
Answer: Store GC Solare Universal Bond at room temperature, between 1-28°C (33.8-82.4°F).
Question: What are the indications for using GC Solare Universal Bond?
Answer: It is indicated for bonding light-cured composites, acid-modified composites (compomers), and dual-cured luting and core build-up composites to tooth structures. Please note that dual-cured materials should be light-cured.
Question: What makes GC Solare Universal Bond unique?
Answer: Its unique formulation includes a dimethacrylate monomer that increases permeability into enamel and dentin compared to other adhesives. It also contains a higher level of phosphate ester monomer to optimize etching.
Question: What is GC Solare Universal Bond?Answer: GC Solare Universal Bond is a dental adhesive designed for bonding light-cured composites and acid-modified composites to tooth structures.
Question: Can this bonding agent be used with orthodontic adhesive ?
Answer: GC Solare Universal Bond is primarily designed for restorative dentistry, not orthodontic applications. It may not be ideal for use with orthodontic adhesive. Orthodontic adhesives typically require specific bonding agents designed for orthodontic procedures to ensure proper adhesion between brackets and teeth, which may have different requirements than restorative bonding agents.
Share